KL-6 Tips: Assess for lung injury and pay attention to lung health signals
The most common respiratory symptoms of COVID 19 patients include dry cough, dyspnea, pneumonia, etc., and in severe cases, white lung can appear, and respiratory failure is life-threatening. Even after rehabilitation, many people still coughed, and many people panicked, and took the initiative to go to the hospital to ask for a film to see the condition of their lungs.
COVID 19 infection can cause bilateral interstitial pneumonia, and 30% to 60% of patients have interstitial lung changes. Compared with nucleic acid testing and chest CT for the detection of COVID-19, the level monitoring of KL-6 expressed on the surface of type II alveolar epithelial cells is rapid and sensitive, and can be used as a useful biomarker to assess the severity of COVID-19 disease.
KL-6 as a novel biomarker for severe COVID-19
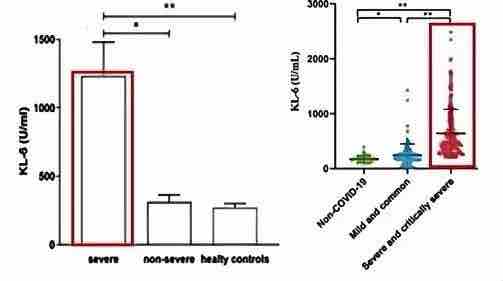
The study found that KL-6 levels were significantly elevated in patients in the severe disease group and were positively correlated with disease severity in COVID-19 patients. The cut-off value of serum KL-6 in patients with severe COVID-19 was 362.65 U/mL, with a sensitivity of 70.4% and a specificity of 95.8%.
KL-6 expedites the diagnostic process for symptomatic cases
In the COVID-19 positive group, the median CT score of patients with KL-6 > 400 U/mL was significantly higher than that of patients with KL-6 ≤ 400 U/mL. CT has high sensitivity and is widely used as an adjunct to the management of COVID-19 patients as a reference diagnostic modality for the assessment of lung involvement and patient stratification. The results of the literature study showed that the dynamic distribution of KL-6 in COVID-19 positive patients was closely related to CT lung severity.
Pulmonary fibrosis & interstitial lung disease
Pulmonary fibrosis is an end-stage change in lung disease characterized by fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix aggregation, which is common in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and is a major group of interstitial lung diseases.
KL-6 Application Department
Rheumatology and Immunology: Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Respiratory: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, COVID-19
Oncology: ICIs-associated pneumonia (CIP), drug-induced pneumonitis, radiation pneumonitis
Pediatrics: Community-acquired pneumonia
ICU versus emergency: differentiating severe pneumonia (pulmonary bacterial infection from pulmonary interstitial lesions)
1. Homogeneous chemiluminescence, no cleaning and no separation
2. 20μL sample, 5 min to produce results
3. Lyophilized reagents, no need for refrigerated storage and transportation
4. Single-serve packaging to avoid reagent waste
评论
发表评论